
As the sun sets on 2G and 3G networks, a new dawn rises for reliable, high-speed connectivity with LTE and 5G. Are you ready to have your equipment migrated to LTE/5G networks?
What is the 2G/3G sunset?
A sunset happens when a technology providers stopped offering one of its products or services. In the context of cellular networks, mobile network operators (MNOs) are shutting down 2G and 3G networks as a result of:
- Obsolete technology: As the world is entering 5G era, 2G and 3G technologies are outdated.
- Spectrum limit: As there is only limited wireless spectrum, older networks must leave the space for newer ones in order to keep (and improve) efficiency of cellular networks.
- Cost saving: Maintaining cellular networks involves huge investments in finance, technical support and other resources. As technology evolves, MNOs are seeking to phase out older generations of networks so that they can offer better services for newer networks.
- Global trend: As the whole world is evolving into 4G and 5G technologies, devices running on older networks are restricted in their ability to run efficiently.
What does 2G/3G sunset mean?
2G/3G sunset is impacting IoT connectivity globally, especially for businesses with IoT devices that rely on 2G/3G networks as their sole source of connectivity. Unless these devices are updated, they will cease to work when the shutdown occurs.
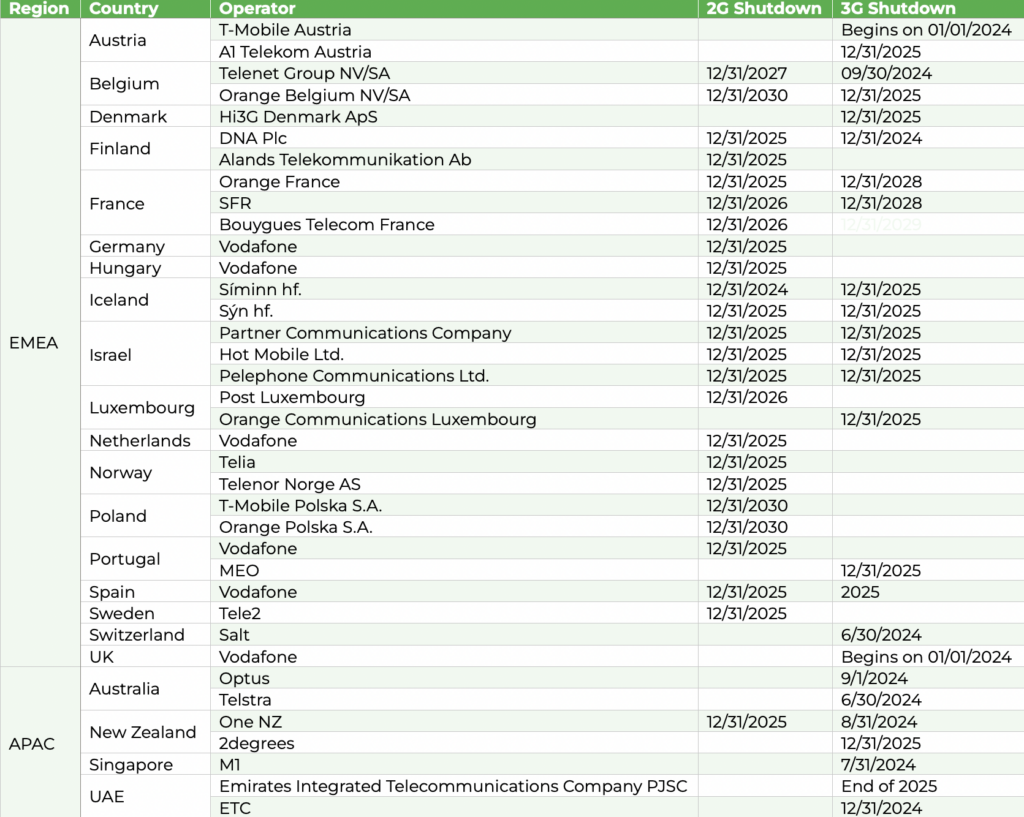
Timeline of 2G/3G sunset
Timelines of 2G/3G shutdown vary across the world. While US carriers have already finished their 2G/3G sunset, the retiring process is still in progress in other regions.
Some upcoming 2G/3G shutdown dates:
How to get prepared for 2G/3G sunset?
- Conduct a comprehensive assessment
To prepare yourself for a smooth network transition, first you need to check the status of your applications. This involves both technology and business.
On the technological side, think about the following questions:
- Active devices: How many 2G/3G devices are still active? How many of your devices need upgrading?
- Bandwidth: What bandwidth is required for your applications? Does your project require fast transfer of large data volumes or simply a steady feed over time?
- Connectivity: What’s the LTE coverage in your target areas? Is the LTE coverage robust enough to ensure efficient operation of your devices?
- Interfaces: How many devices are you collecting data from? How many and what kind of interfaces (Ethernet ports, serial ports, I/O, etc.) are required?
From business side, ask yourself:
- Data plan: What data plans are available from MNOs? Which plan is more cost efficient?
- Budget: What is the expected cost for LTE migration?
- Timeline: How long will it take to migrate to LTE?
- Choose the right LTE equipment
Select LTE routers and gateways that suit your specific requirements. Here are some considerations when choosing your equipment:
- Network type: Figure out what network types are required for your project (LTE CAT4/CAT1/CAT M1). It is always recommended to choose hardware with multiple network options for different use cases.
- Performance: Look for industrial-grade products with reliable performance in varying environments.
- Global certification: Ensure that the selected equipment is globally certified to meet regulatory standards.
- Ease of installation: Opt for equipment designed for ease of installation and minimal configuration changes. Consider plug-and-play solutions for a smoother deployment process.
- Security measures: Implement robust data protection measures to safeguard against cybersecurity threats.
- Technical support: Choose a vendor that offers reliable before and after-sales support and maintenance services.
- Develop a detailed migration plan
Seek guidance from network professionals or your equipment provider to develop a migration plan tailored to your business needs. Develop a detailed roadmap that outlines each step of the migration, considering potential downtime and contingency plans.
- Test and monitor
After deployment, conduct thorough testing of network performance, connectivity, and data flow. Implement remote monitoring tools for continuous observation, allowing quick identification and resolution of potential issues.
- Stay informed for future upgrades
Stay updated on emerging technologies and industry trends to make informed decisions for future network upgrades.
Find your alternatives to 2G/3G solutions
- LTE CAT4
With downlink speeds of up to 150 Mbps and enhanced uplink speeds, LTE CAT4 ensures faster data transfer, facilitating seamless communication with multiple devices. It is suitable for a wide range of applications, including mobile broadband, IoT (Internet of Things) devices, video streaming, and other data-intensive tasks.
- LTE CAT1
LTE CAT1 is the closest alternative to 2G and some 3G applications in terms of capability (voice, data, SMS, speed) and roaming across multiple networks and countries. It is a good fit for many single-device IoT applications such as digital signage, kiosks, industrial controllers and security cameras.
- LTE CAT M
LTE CAT M is an energy-saving solution for battery or solar powered applications. It fits traditional 2G applications and devices that require mobility, such as asset trackers and IoT sensors.
- NB-IoT
NB-IoT is a highly energy efficient solution best suited for stationary sensor devices that send only very small amounts of data and in scenarios where real time is not mandatory and other technologies would struggle to get a signal.
Goodbye 2G and 3G
In bidding farewell to 2G and 3G, the road to successful LTE migration involves strategic planning, expert guidance, and ongoing commitment. Through careful planning and a collaborative spirit, businesses can usher in a future marked by the speed, reliability, and versatility of LTE technology.